
|
ZÂKHÔ TO DIYÂRBEKR
May 10—June 4
THE Babylonians, and after them the Nestorians and the Moslems, held that the Ark of Noah, when the waters subsided, grounded not upon the mountain of Ararat, but upon Jûdî Dâgh. To that school of thought I also belong, for I have made the pilgrimage and seen what I have seen. The snows that gleamed upon us from under the skirts of the thunderstorm when we camped at Zâkhô were the spring-time wreaths of Jebel Jûdî, and resisting all other claims, we turned our faces towards them on the following day. Selîm, the muleteer, gloried in this decision. He was a native of the hills above Killiz, and like all mountain people his spirits rose with the rising ground. Above Zâkhô the Khâbûr is spanned by a masonry bridge of four arches (Fig. 181), but when we came to Durnakh, we found the Heizil Sû innocent of bridge or ferry-boat. The river, which is the principal affluent of the Khâbûr, ran deep and swift by reason of the melting snows. In midstream its waters touched the top of my riding-boots and buffeted my mare, so that I thought she would certainly fall; indeed she would have fallen but for two of the inhabitants of Durnakh who, with garments rolled round their waists, held bravely up her chin. Another pair was attached to each of the baggage animals, the muleteers joined in the sport, and we reached the further side without loss. Four hours and a half from Zâkhô we passed by Tell Kobbîn, an ancient mound with a village of the same name a little further to the north,1
---------------------------
and in two hours more we / p.290 / entered the foothills and lunched in an oak grove near the village of Gerik. Our path led us over rising meadows to Geurmuk and Dadar, and so into the mouth of a gorge where Hasanah nestles under rocky peaks. The clouds gathered over the mountains and thunder came booming through the gorge as we pitched our tents by the edge of the stream, nine hours from Zâkhô. Hasanah is a Christian village inhabited partly by Nestorians and partly by the converts of American missionaries. The pastor of the Protestant Nestorians, if I may so call him (when I asked him what was his persuasion, he replied that he was Prôt), came at once to offer his respects, coupled with a bunch of pink roses from his garden, and I, being much attracted by his sturdy figure and simple open countenance, asked him to guide me next day through the hills. Over and above his personal charms, Kas Mattai had the advantage of a knowledge of Arabic. He spoke besides Kurdish and Syriac, but his native tongue was Fellâhî (the Peasant Language), which is no other than Assyrian. His brother Shim'ûn, who accompanied us on all our expeditions (he climbed the rocks like a cat or a Grindelwalder), had nothing but Fellâhî and Kurdish and a cheerful face, but with one or the other, or all three, he made his way deep into my affections before we parted. We walked up the narrow valley, where flowers and flowering shrubs nodded over the path in an almost incredible luxuriance, and climbed the steep wooded hill-side to a point where the rock had been smoothed to receive the image of an Assyrian king, though none had been carved upon it. Above it rose a precipitous crag clothed on one side with hanging woods through which zigzagged a very ancient path, lost at times among fallen rocks and trees, while at times its embankment of stones was still clearly to be traced. On the summit of the crag were vestiges of a small fortress. The walls were indicated by heaps of unsquared stones, many of which had fallen down the hill, where they lay thickly strewn; the evidence afforded by them, and by the carefully constructed path, made it certain that we were standing upon the site of some watch-tower that had guarded the Hasanah gorge. On the opposite side rises a second crag whereon, said
1 Ainsworth thinks that it may mark the site of the village at which the Greeks camped on the second day from Zâkhô: Travels in the Track, p. 146. Xenophon mentions neither the Khâbûr nor the Heizil.
---------------------------
[ Illustrations opposite p.290 ]

|

|
[ Illustration opposite p.291 ]

|
/ HASANAH p.291 / Kas Mattai, are ruins of the same description. That the valley was held by the Assyrians there can be no doubt, for it is signed with their name. Below and to the west of the crag to which we had climbed there is another smoothed niche in the rock (Fig. 182), and here the work has been completed and the niche is carved with the figure of an Assyrian king, wearing a long fringed robe and carrying a sceptre.1
---------------------------
1 Mr. King, who has visited Jûdî Dâgh, tells me that all the reliefs are of Sennacherib and were carved in the year 699 B.C.
---------------------------
At a later age, the mountains had been occupied by Christians. Kas Mattai showed me at the foot of the crag a few vaulted chambers which he declared to be the ruins of a Nestorian monastery, and walking westward for an hour or more along the wooded ridges, we came to a second and larger monastic ruin, with a garden of fruit-trees about it, and groves of tall blue irises which had escaped from the cemetery of the monks and wandered over the hill-side.
In the high oak woods I forgot for a few hours the stifling heat which had weighed upon us ever since we had left Môsul. Each morning we had promised one another a cooler air as we neared the mountains; each evening the thermometer placed in the shade of my tent registered from 88° to 93° Fahrenheit. The heavy air was like an enveloping garment which it was impossible to cast off, and as I walked through the woods I was overmastered by a desire for the snow patches that lay upon the peaks — for one day of sharp mountain air and of freedom from the lowland plague of flies. Sefînet Nebî Nûh, the ship of the Prophet Noah, was there to serve as an excuse.
Accordingly we set out from camp at four o'clock on the following morning. Kas Mattai and Shim'ûn in their felt sandals, raishîkî, a proper footgear for the mountaineer, Selîm, whom Providence had marked out for the expedition, 'Abdu'l Mejîd, a zaptieh from Zâkhô, who had been ordained as pointedly to walk upon flat ground, and the donkey. "As for that donkey," said Fattûh, "if he stays two days in the camp eating grass. Selîm will not be able to remain upon his back." He was Selîm's mount, and Selîm, who knew his mind better than any other among us, was persuaded that he / p.292 / would enjoy the trip. The donkey therefore carried the lunch. We climbed for two hours and a half through oak woods and along the upper slopes of the hills under a precipitous crest. But this was not what I had come out to see, and as soon as I perceived a couloir in the rocks, I made straight for it and in a few moments stepped out upon an alp. There lay the snow wreaths; globularia nudicaulis carpeted the ground with blue, yellow ranunculus gilded the damp hollows, and pale-blue squills pushed up their heads between the stones and shivered in the keen wind. Selîm had followed me up the couloir.
"The hills are good," said he, gathering up a handful of snow, "but I do not think that the donkey will come up here, nor yet 'Abdu'l Mejîd."
We returned reluctantly to the path and walked on for another half-hour till Kas Mattai announced that the Ark of Noah was immediately above us. Among asphodel and forget-me-nots we left the zaptieh and the donkey; Selîm shouldered the lunch-bags, and we climbed the steep slopes for another half-hour. And so we came to Noah's Ark, which had run aground in a bed of scarlet tulips (Fig. 184).
There was once a famous Nestorian monastery, the Cloister of the Ark, upon the summit of Mount Jûdî, but it was destroyed by lightning in the year of Christ 766.1
---------------------------
1 Ritter, Vol. XI. p. 154.
---------------------------
Upon its ruins, said Kas Mattai, the Moslems had erected a shrine, and this too has fallen; but Christian, Moslem and Jew still visit the mount upon a certain day in the summer and offer their oblations to the Prophet Noah. That which they actually see is a number of roofless chambers upon the extreme summit of the hill. They are roughly built of unsquared stones, piled together without mortar, and from wall to wall are laid tree-trunks and boughs, so disposed that they may support a roofing of cloths, which is thrown over them at the time of the annual festival. To the east of these buildings there is an open court enclosed by a low stone wall. The walls both of the chambers and of the court are all, as I should judge, / NOAH'S ARK p.293 / constructions of a recent date, and they are certainly Mohammadan, since one of the chambers contains a mihrâb niche to the south, and in the enclosing wall of the court there is a similar rough niche. Further to the west lie the ruins of a detached chamber built of very large stones, and perhaps of an earlier date. Beneath the upper rocks upon which these edifices stand, there is a tank fed by the winter snows which had not entirely disappeared from the mountain-top. Still further down, upon a small plateau, are scattered fragments of a different architecture, carefully built walls, stone doorposts, and lintels showing above the level of the soil. Here, I make little doubt, was the site of the Nestorian monastery.
The prospect from the ziyârah was as wild, as rugged and as splendid as the heart could desire, and desolate beyond measure. The ridge of Jûdî Dâgh sinks down to the north on to a rolling upland which for many miles offers ideal dwelling-places for a hardy mountain folk. There were but four villages to be seen upon it. The largest of these was Shandokh, the home of a family of Kurdish âghâs whose predatory habits account for the scantiness of the population. To the east of it lay Heshtân, which is in Arabic Thamânîn (the Eighty), so called because the eighty persons who were saved from the Deluge founded there the first village of the regenerated world when they descended from Jebel Jûdî.1
---------------------------
1 So said Kas Mattai, but the Arab geographers would seem to place it to the south of Jûdî Dâgh, not to the north. For example, Mukaddasî says that Thamânîn, the village of the eighty who were saved from the flood, stands on the river Ghazil (the Heizil Sû), a day's march from Hasanîyeh (Zâkhô), ed. de Goeje, pp. 139 and 149. Sachau, however, speaks of Bêtmanîn as being behind Jûdî Dâgh, i.e. he bears out my information: Reise, p. 376.
---------------------------
Further to the north an endless welter of mountains stretched between us and Lake Vân. They rose, towards the east, into snowy ranges, and very far to the south-east we could see the highest snow-peaks of Tiyârî, where the Nestorians, grouped under a tribal system, defend their faith with their lives against the Kurdish tribes — a hereditary warfare, marked with prodigies of valour on the part of the Christians, and with such success as the matchlock may attain over the Martini rifle.
/ p.294 /
Because the light air breathed sharply off the snows, and because the vista of mountains was a feast to the eye, we lay for several hours in the sanctuary of the Prophet Noah. There can be no manner of doubt that I ought to have completed the pilgrimage by visiting his grave, but it lay far down upon the southern slopes of Jûdî Dâgh, and I was making holiday upon the hill-tops; therefore when we turned homewards, we bade Shim'ûn conduct the donkey and 'Abdu'l Mejîd to Hasanah and ourselves kept to the crest of the ridge. Half-an-hour from the summit we met some Kurdish shepherds near a small heap of ruins, concerning which they related the following history: Once upon a time there was a holy man who took a vow of pilgrimage to the ship of Noah, and for a month he journeyed over hill and vale until he reached the spot on which we stood. And there he met the Evil One, who asked him whence he came and whither he was going. The holy man explained that he was bent on a pilgrimage to the ship of Noah. "You have still," said the Devil, "a month's journey before you." Thereat the pilgrim, being old and weary, lost heart, and since he could not return with his vow unfulfilled, he built himself a hut and ended his days within sight of the goal, if his eyes had not been too worn to see. The presence of the shepherds upon Mount Jûdî was not to be attributed to any pious purpose. They had come up from the villages below to escape from the sheep tax which was about to be levied for the second time within a twelvemonth, once for last year's arrears, and once for this year's dues. Their lawless flocks skipped among the boulders and the snow-wreaths as light-heartedly as the wild goat, which no government can assess, but the owners lived in anxiety, and when, half-an-hour further, we encountered a second company, they took us for soldiers and greeted us with rifle shots. Kas Mattai grasped the situation and shouted a justification of our existence, which was not received without hesitation. I was standing, when the shots began, in the middle of a névé, and thinking that I must offer a fine mark, I stepped off the snow and sat down upon a grey rock to await developments. But as soon as we had made it clear that we / JÛDÎ DÂGH p.295 / were simple people with no official position, we were allowed to pass. "It was well," observed Kas Mattai, as we clambered down the crags, "that 'Abdu'l Mejîd was not with us. They would have killed him."
At the foot of the rocks we sat down to rest beside a bubbling spring.
"Have you suffered at the hand of the government?" I asked my guide.
"We suffer from the Kurds," he replied, "and there is no one to protect us but God. Effendim, the âghâwât, and their mares, and the followers they bring with them? And how shall we refuse when they are armed with rifles?"
"Have you no arms?" said I.
"We have no money to buy rifles," he answered; "and if we bought them, the Kurds would take them from us. And when we have killed our last sheep that we may entertain them, they seize upon all we possess before they leave us."
"Oh Merciful!" ejaculated Selîm.
"Sir," said Kas Mattai, "last year they took my bed, and that which was too worthless to carry away they broke and threw upon the fire. But if we resisted they would burn the village."
We ran down through the oak woods and got into camp at four in the afternoon.
"God prolong your existence!" cried Fattûh. "Have you seen the ship of the Prophet Noah?"
"Oh Fattûh," I replied, "prepare the tea. I have seen the ship of the Prophet Noah." So it is that I subscribe in this matter to the wisdom of the Kurân: "And immediately the water abated and the decree was fulfilled and the Ark rested upon the mountain of Jûdî."
Next morning the camp was sent straight to Jezîreh, which it reached after a six-hours' march, but I, with Shim'ûn as guide, followed the line of the hills. We rode for two hours through the oak woods, and then crossed a gorge wherein / p.296 / lies the Moslem village of Evler. The incomparable beauty of these valleys passes belief. Evler was buried in a profusion of pomegranate and walnut, fig, almond and mulberry trees; the vines were wreathed from tree to tree, the ground beneath was deep in corn, and the banks of the stream aglow with oleander. An hour further we reached the Nestorian village of Shakh, where a ruined castle protects the entrance of the gorge. The walls climb up the hillside towards a citadel placed upon a high peak; above the village two deep valleys run up into the mountains, and each has been walled across, so that Shakh was guarded from attack on every side. I should judge these fortifications to be Kurdish, but there are traces of an older civilization on the rocks above them (Fig. 183). Of the four Assyrian reliefs that are reported to exist, I saw only three, the fourth being cut upon the face of the cliff and unapproachable except with ropes. Each of the three niches which I was shown (after an hour's climb in the hottest part of the day) contained a single figure, like that of Hasanah; each had been covered with cuneiform inscriptions, but in two cases both the figure and the inscriptions had all but weathered away. We left Shakh at midday, stopped for half-an-hour to lunch by the stream, and reached Jezîret ibn 'Umar at four o'clock. The camp was pitched upon a high bank overhanging the Tigris, but the bridge of boats which should have connected us with the town was broken, and I crossed by a ferry on the following day.
Jezîret ibn 'Umar is built upon an island formed by the Tigris and a small loop canal. It is called after a certain Hassan ibn 'Umar of the tribe of Taghlib, who lived in the ninth century.1
---------------------------
1 It has been identified with the Bezabde of Ammianus Marcellinus, the Saphe of Ptolemy (ed. Mûller, p. 1005), and the Sapha of the Peutinger Tables. Ammianus Marcellinus is generally supposed to have confused Bezabde-Jezîreh with Phœnice-Finik, saying that the two names are applied to the same place. In his account of the capture of Bezabde by Sapor II, in A.D. 360, his description applies better to Finik than to Jezîreh (Bk. XX. ch. vii. I. See, however, Hartmann: Bohtân, Part II. p. 98). He relates further that Constantius attempted in vain to re- / p.297 / capture Bezabde (Bk. XX. ch. xi.), but in this passage he must mean Jezîreh. I can find little in the history of Jezîreh except the mention of sieges: by Tîmûr for example (Ritter, Vol. IX. p. 709), and by the emirs of Bohtân (Rich: op. cit., Vol. I. p. 106). When Moltke visited it in 1838 it was a heap of ruins (Briefe aus der Turkei, Berlin, 1893, p. 251), and it was not much more when I saw it.
---------------------------
/ p.296 / upon the river's edge stands a much-ruined
[ Illustrations opposite p.296 ]

|

|
[ Illustrations opposite p.297 ]

|

|
/ SHAKH p.297 / castle of which the masonry is mostly of alternate bands of black basalt and white limestone. Over one of the doors are carved a couple of rudely executed lions (Fig. 185). The town walls still exist in part and belong to the same date as the castle; so too does the fragment of a masonry bridge which spanned the Tigris about half-an-hour's ride below the town (Fig. 186). On our way to it we forded the moat which was at that time quite shallow. One of the bridge piers is decorated with a key pattern of black and white stone, and with some curious reliefs representing the signs of the zodiac, of which the work is similar in character to that of the lions upon the castle gate (Fig. 188). Each relief bears an inscription in Arabic naming the zodiacal sign which it depicts.1
---------------------------
1 Sachau notices these reliefs. In his opinion the inscriptions are of no great age: Reise, p. 379.
---------------------------
As we came back through the town we stopped at the principal mosque, which has a pair of fine bronze doors, with bronze knockers worked in a design of intertwined dragons. A small dome, set upon columns that may have been taken from an earlier building, covers the fountain in the courtyard (Fig. 187).2
---------------------------
2 Ibn Batûtah, in the fourteenth century, mentions an old mosque in the market place, which is probably the same as the one I saw, though it has undergone many alterations and reparations since his day.
---------------------------
Jezîret ibn 'Umar has a bad reputation for the fever which is bred in its marshy moat; moreover it was stifling hot. I hurried through a cursory sight-seeing and ferried back to the opposite bank, where I found the baggage animals loaded and ready to start. Having followed the Tigris bank for half-an-hour, I left the caravan to pursue its way to Finik and turned up the valley of the Risür Chai. In less than two hours from Jezîreh we came to a ruined Kurdish fort, standing on either side of the stream and blocking effectually the passage of the gorge; / p.298 / and carved upon the rocks of the left bank there is a more ancient guardian of the pass, a warrior armed, and mounted upon a bounding horse (Fig. 189). His companion, who went on foot, has fallen into the stream, and I know no other record of him than Layard's woodcut.1
---------------------------
1 Nineveh and Babylon, p. 55
---------------------------
The figure of the horseman is much defaced by time. The winter rains have worn thin his armour, the spring floods have undermined the rock on which he stands, but shadowy though his image may be, it marks the triumph of a European civilization, and its prototypes are to be sought not among the bearded divinities and winged monsters of Assyria, but in the work of Western sculptors. The Parthian, who was the bitter enemy of the Roman empire, carved it upon the rocks of Kasr Ghelli, and bore witness with his own hand to the overmastery of Roman culture.
We cut across the hills back to the Tigris, and rode by a memorably inadequate path — equally memorable for the profusion of oleanders through which it ran — up the bank to Finik. The high ground on either side of the valley falls sharply to the water, and the river bursts here through the last barrier of mountain which divides it from the Mesopotamian plain. Finik has been from all time the key of the ravine. Before we reached the side-gorge in which the village lies, we passed a great enclosure of ruined walls and towers, and below it, among the ricefields that occupy a cape jutting into the stream, there are remains of similar fortifications. Beyond the gorge of Finik we rode under a crag which is crowned by the most commanding of the many castles, and less imposing fortress ruins are clustered about its foot. We made our way through groves of pomegranate down to the camp, pitched in clover pastures by the river. A ferry-boat was drawn up upon the bank, and with its help we designed to convey ourselves next morning to the further side, but the boat was ancient and the stream swift, and I suspected that the passage would be a long business. Therefore I left Fattûh to cope with the ferrymen and went up, while he did
[ Illustrations opposite p.298 ]

|

|
[ Illustration opposite p.299 ]

|
/ FINIK p.299 / so, to the village. A tumbling stream and masses of oleander fill the gorge; the greater part of the inhabitants of Finik are lodge in caves, preserving, no doubt, the customs of their remotest ancestors whose rock-cut dwellings they have inherited.1
---------------------------
1 The caves are carefully excavated and I should say that they are ancient. Layard (Nineveh and Babylon, p. 54) speaks of them as tombs and some may have been intended as burial-places, but I do not doubt that many were from all time used by the living. The troglodyte habits of the dwellers in these mountains are still strongly marked. Above Bâ'adrî I saw an underground village; at Hisn Keif, higher up the Tigris, the people live in rock-hewn chambers.
---------------------------
We climbed up to the castle by a winding path and entered it on the side furthest from the Tigris, the face of the hill turned towards the river being a precipitous rock. The castle wall is partly of masonry and partly of the natural rock, and the gate is tunnelled through the cliff and flanked by small rock-cut chambers. Within the enclosure there are a number of underground chambers, and on the highest peak the rooms are rock-hewn and vaulted with masonry. How old the rock cutting may be I cannot tell; the masonry is not very ancient, some of it may be modern, while none could safely be dated earlier than the Middle Ages. But the position overhanging the Tigris is superb, and it is difficult to think that the Phœnice which Sapor overthrew stood on any other crag. The rolling plateau of the Tûr 'Abdîn stretched away to the south-west, and since I observed that the ferrying of my caravan was taking as long a time as I had anticipated, I sat down and made a comfortable survey of the country we were about to traverse. We returned to the village by the way we had come (there is no other) and climbed the rocks on the opposite side of the valley, where Layard found a much-effaced Parthian relief. It depicts the figures of a man and a woman, clad in short tunics which hang in heavy folds over loosely-fitting trousers (Fig. 190). Above the man's head are traces of an inscription which even in Layard's day was indecipherable. Our guide hurried back to the village while I was examining the tablet, and when we came down we found him spreading a meal of omelets and bread and bowls of irân (a most delectable drink made of sour curds / p.300 / beaten up in water) under the shade of some mulberry-trees — a welcome sight to those who have breakfasted early and climbed over many rocks. A less pleasing surprise awaited us when we reached the Tigris; not half the horses had crossed, and the ferry-boat was engaged in intricate and lengthy manœvres on the opposite side. There was nothing to be done but to wait for its return, and I lay down among the clover under a hawthorn-bush.
It was here that we were to bid a final farewell to the Greeks who had accompanied us from the outset of the journey (Fig. 191). "When they had arrived at a spot where the Tigris was quite impassable from its depth and width, and where there was no passage along its banks, as the Carduchian mountains hung steep over the stream, it appeared to the generals that they must march over those mountains, for they had heard from the prisoners that if they could cross the Carduchian heights they would be able to ford the sources of the Tigris in Armenia."1
---------------------------
1 Anabasis, Bk. IV. ch. i.
---------------------------
They turned north, therefore, and fought their way through the land of the Carduchi, which are the Kurds, until they reached the sea, while we, having a ferry-boat at our disposal and a smaller force to handle, passed over the Tigris into the Tûr 'Abdîn. So at length we parted, and Cheirosophus in advance with the light-armed troops scaled the hills of Finik and led slowly forward, leaving Xenophon to bring up the rear with the heavy-armed men. Their shields and corselets glittered upon the steep, they climbed, and reached the summit of the ridge, and disappeared. . . .
"Effendim!" Fattûh broke into my meditations. "Effendim, the boat is ready."
"Oh Fattû," said I, "the Greeks are gone."
Fattûh looked vaguely disturbed.
"The Greeks of old days, who marched with us down the Euphrates," I explained.
The history of the Ten Thousand is not included in the Aleppine curriculum, and since Fattûh can neither read nor / FINIK p.301 / write, he is debarred from supplementing the acquirements of his brief school-days, but he searched his memory for fragments of my meaningless talk.
"Those?" he said. "God be with them!"
We had more reason to invoke the protection of the Almighty on our own behalf. The ferry-boat was packed with our baggage animals, standing head to tail; the current was very swift. We shot down it, heading aslant, until we neared the further shore; the ferrymen thrust their long poles sharply into the water, and the boat heeled round until the gunwale touched the level of the stream. Thereat the horses tumbled over like ninepins, one upon the other, and I, sitting high in the stern, was saved by the timely clutch of a zaptieh from plunging headlong into the stream. "Allah, Allah!" cried the ferrymen, and we ran aground upon the bank.
The Tûr 'Abdîn, which we now entered, is a lofty plateau that stretches from Finik on the east to Mardîn and Diyârbekr on the west, and south to Nisîbîn. The Tigris embraces it to north and east; on the south side the heights of the plateau fall abruptly into the Mesopotamian deserts which, interrupted only by the long hog's back of the Jebel Sinjâ, extend to the Persian Gulf. The Mount of the Servants of God — such is the meaning of its beautiful name — was known to the ancients as Masius Mons and Iazala Mons, Mount Izala occupying the eastern end of the plateau.1
---------------------------
1 Ammianus Marcellinus, when he speaks of Izala, evidently intends the name to cover the whole Tûr 'Abdîn: Bk. XVIII. ch. vi. 11, and Bk. XIX. ch. ix. 4.
---------------------------
This country lay upon the confines of the Roman and the Persian empires, and in the confused accounts of the campaigns of Constantius, Justinian and Heraclius the frontier fortresses of Izala and Masius play a conspicuous part. While war raged round Amida, Marde, Dara and Nisibis, the secluded valleys of the Tûr 'Abdîn were falling peacefully into the hands of the Servants of God. The Mount was a stronghold of the Christian faith; monastery after monastery rose among the oak woods, the rolling uplands were cleared and planted with / p.302 / vineyards, and the ancient communities of the Eastern Church multiplied and grew rich in their almost inaccessible retreat.1
---------------------------
1 The Jacobites and the Syrians (i.e. Jacobites who have submitted to Rome) have now ousted the Nestorians, who must have been the first to occupy the Tûr 'Abdîn. When this change took place I do not know, but the Nestorians were in possession of the monastery of Mâr Augen as late as 1505: Pognon, op. cit., p. 109.
---------------------------
Very little has been published concerning the architectural remains of the district, but I had happened to see in Môsul some photographs which had awakened my curiosity, and the Dominican fathers whom I met at Baviân had raised it still higher.2
---------------------------
2 Pognon's account of the churches, and his publication of the inscriptions, is the best work on the subject (Inscriptions de la Mêsopotamie); Parry (Six Months in a Syrian Monastery) gives a short description of the churches and some sketch plans.
---------------------------
The morning was half spent before we landed on the west bank of the Tigris. our path climbed up on to the plateau and led us over downs sweet scented with clover and very thinly populated: during the five hours' journey from the Tigris to Azakh we saw only three villages.3
---------------------------
3 Tigris ferry 9.25; Handak (Christian) 9.45; Thelailah (Moslem) 10.40; Kôdakh — marked in Kiepert — we saw at 12.15, a little to the south of our route.
---------------------------
Azakh, where we camped, is inhabited mainly by Jacobites, some of whom have modified their creed under the influence of American missionaries. The Protestant pastor paid me a visit and brought disquieting news. While we were still at Môsul we had heard rumours of a massacre of the Christians which had taken place at Adana. The Tûr 'Abdîn was full of these reports. It was impossible to make out whether the events which were related to us were past or present, how serious the massacre had been or whether it were now at an end, and it was not until I reached Cæsarea that I learnt the truth with regard to the double outbreak in Cilicia. For a month we were greeted wherever we went with details of fresh calamities that were in part the reverberation of those of which we had already heard, and everywhere these histories were accompanied by the assurance that a deliberate attempt had been / AZAKH p.303 / made from without to stir up massacres in the districts through which we passed. No direct proof of this statement was offered; I never met the man who had set eyes on the reported telegram, nor any one who could tell me what signature it bore. But in the East, conviction does not wait upon evidence. I learnt to realize the evil power of rumour, and experience taught me how hard it is to keep the mind steadily fixed upon the proposition that two unsupported statements (or the same often repeated) will not make a certainty. The atmosphere of panic which surrounded us is the true precursor of disaster, and I found good reason to respect the statecraft of the Turkish officials whose firmness saved the population from the consequences of their own loudly expressed suspicions. I bear testimony to the fact that all that I saw or heard of the agitation which attended the events of April 1909 led me to the conviction that the local authorities had set their face against bloodshed, and by so doing had averted it.
Next morning we rode for six hours to Bâ Sebrîna, over wide uplands almost entirely uncultivated and covered with small oak-trees. The country was so like the swelling, thinly wooded hills that lead out of the Belkâ towards the Syrian Desert that at times I could have sworn that we were riding from Gilead into Moab.1
---------------------------
1 Our itinerary was as follows: 5.30 Azakh; 6.30 a ruined site (marked in Kiepert); 7.5 Salakûn (Kiepert: Salekon Kharabe), a small Moslem village; 8 Middo (marked in Kiepert), a Christian village on the further side of a deep gorge (here we got into the oak woods); 9 Irmez, about a mile to the south of our road; 9.25 Arba', a Christian village also about a mile south; 9.45-10.45 Deir Mâr Shim'ûn, a ruined monastery; 11.30 Deir Bar Sauma, the first monastery of Bâ Sebrîna.
---------------------------
The characteristic feature of the Tûr 'Abdîn is the absence of streams; even when we crossed a deep valley, as we did twice during the course of the morning, there was no running water in it. The water supply of the villages is derived from pools which are fed by the winter rains and snows. In the second valley we found the ruined monastery of Mâr Shim'ûn, placed among thickets and deep herbage, but, to my disappointment, it was of little architec- / p.304 / tural interest. The village of Bâ Sebrîna is wholly Christian. it has been an important place and though it has now fallen to the estate of a small hamlet, it contains innumerable monasteries. Several of these are beyond the limits of the town. They lie, each in its own enclosing wall, like small forts upon the hills, and each is garrisoned by a single monk. The monastic buildings are exiguous, and I doubt whether they can have been intended for more than one or two persons; perhaps they should be regarded as clerical rather than as monastic foundations,1
---------------------------
1 Monasteria clericorum. See The Thousand and One Churches, p. 461.
---------------------------
and the living-rooms were intended for the lodging of those who served the shrine. The first monastery which we reached upon the outskirts of Bâ Sebrîna was of this character. Its high and rather tapering rectangular tower, and strong walls, gave it from afar a striking appearance, but the vaulted chapel and the rooms set round a tiny court were rudely built of undressed stones, almost totally dark, and devoid of decorative features. I looked at several of the monastic houses within the village, and always with the same results: they had no pretension to architectural interest and were without ornament or inscriptions by which to determine their date. But at the monastery of Mâr Dodo I found a clue to the history of Bâ Sebrîna. The church, which is the largest in the place, stands upon the north side of a walled court round which are placed insignificant living-rooms, store-rooms and stables. The church consists of a closed narthex running along the south side of a vaulted aisleless nave, with a single apse to the east. On the east side of the court, south of the church, there is an exedra covered by a semi-dome and provided with a stone reading-desk on which to set the holy books. All the masonry is rude and unskilful, and the carved capitals and moulded arch of the exedra bear no sign of great antiquity, while the engaged capitals in the church are merely blocked out. Now this scheme of a single-chambered church, with a narthex to the south and an external exedra, filled me with amazement, for it was unlike any that I had seen, but I was / BÂ SEBRÎNA p.305 / subsequently to learn that it is one of the oldest ecclesiastical plans of the Tûr 'Abdîn, and its combination at Bâ Sebrîna with rough masonry and late decorative details is explained by a Syriac inscription above the porch which states that the church was built in the year 1510 of the Seleucid era, i.e. A.D. 1200. Whether this be the date of the first foundation or of a fundamental reconstruction upon an older site I cannot be certain, though from the absence of all trace of early work I incline to the former alternative, and I conclude that the old architectural scheme of the Tûr 'Abdîn was adhered to closely at a later date, when a second period of building activity saw the foundation of the churches and monasteries of Bâ Sebrîna. But since I did not then know that these edifices were exact copies of more ancient work, their recent date was a rude shock, and I began to wonder whether the Mount would prove to be as fruitful a field as I had hoped. Bâ Sebrîna, at any rate, had been drawn blank, and we rode down for three-quarters of an hour through vineyards to the village of Sâreh. As soon as we had settled upon a camping-ground — no easy matter on account of the interminable vineyards — I walked down to the village to examine the church. The âghâ of Sâreh belongs to one of the leading Kurdish families of these parts. I found him in an open space near the church, entertaining friends who had ridden over from a neighbouring village. They too were âghâs of a noble house, and they were tricked out in all the finery which their birth warranted. Their short jackets were covered with embroidery, silver-mounted daggers were stuck into their girdles, and upon their heads they wore immense erections of white felt, wrapped round with a silken handkerchief of which the ends stuck out like wings over their foreheads. They pressed me to accept several tame partridges which they kept to lure the wild birds, and while we waited for the priest to bring the key of the church, they exhibited the very curious stela (Fig. 192) which stands upside down in the courtyard.1
---------------------------
1 Pognon: op. cit., p.108. the stela has not, as Pognon feared, been destroyed. The script is in an unknown alphabet, which Pognon believes / p.306 /to be the prototype of Pehlevî. He gives excellent photographs of the two inscriptions; my photograph shows the relief on the third side. The fourth side is much weather-worn.
---------------------------
/ p.305 / Meantime the village priest had arrived, and I / p.306 / followed him unsuspiciously into the church. But I had not stood for more than a minute inside the building than I happened to look down on to the floor and perceived it to be black with fleas. I made a hasty exit, tore off my stockings and plunged them into a tank of water, which offered the safest remedy in this emergency.
"There are," said the priest apologetically, "a great many, but they are all swept out on Sunday morning. On Sunday there are none."
I confess to a deep scepticism on this head.
The incompleteness of the maps and the absence of trustworthy information led us far astray upon the following day. I had heard of a very ancient monastery that lay upon the outer edge of the Tûr 'Abdîn: upon the way thither I proposed to visit the castle of Hâtim Tâi. Accordingly I spread out Kiepert, and drawing a bee-line across the blank paper, told Fattûh to take the camp to Useh Dereh (Kiepert calls it Useden), and provided him with a zaptieh and a guide. Another villager accompanied Jûsef and me and the second zaptieh, and undertook to guide us via the castle to Useh Dereh. We set forth from Sâreh at 5.30 and rode through uninhabited oak woods till 8.10, when we reached a ruined village from which we could see the castle of Hâtim Tâi standing up boldly on the opposite side of a deep valley. There was no road by which to reach it — not so much as a bridle path. We struggled down through the woods, dragging our horses over rocks and fallen trees, and by the special mercy of Providence reached at 9.15, and without accident, the foot of the castle hill. A path led round it to the Yezîdî village of Gelîyeh, and thither I sent Jûsef and the zaptieh with the horses, while the man of Sâreh climbed the hill with me. Hâtim Tâi was a renowned sheikh of the Arab tribe of the Tâi, but the castle which is called after him has a far longer history. The summit of the hill is enclosed in a
[ Illustrations opposite p.306 ]

|

|
[ Illustrations opposite p.307 ]

|
/ HÂTIM TAI p.307 / double line of fortification following the contours of the slopes. The lower ring is provided with towers at the angles of the wall, and with round bastions of very slight projection. Within the inner enclosure stands the citadel, now completely ruined and bearing evidences of frequent reconstruction. The oldest parts are unmistakably of Byzantine masonry, and contain a chapel of which the apse is well preserved (Fig. 193). The castle must have been rebuilt during the Mohammadan period, and then again rebuilt, for in one of the walls of the citadel there is a fragment of an Arabic inscription, which is not in its original position, neither is the inscription complete.1
---------------------------
1 I sent the photograph to Professor van Berchem. The inscription is merely a date: 630 (=A.D. 1232-3), or possibly 639.
---------------------------
the Yezîdîz declare that the castle was one of their strongholds until it passed into the hands of the Tâi, and this might account for a reconstruction of the citadel at a late period. The only other inscription which I could find is also Arabic. It is apparently a name, with no date or further qualification, cut upon the main gate of the outer wall.2
---------------------------
2 The name itself is unintelligible.
---------------------------
In the space between the two walls there are a number of small rock-hewn cisterns, some of which were probably intended to hold corn and other provisions. The main water supply was drawn from the large cistern in the citadel. So far as I could judge, the ruins, therefore, exhibit Yezîdî or Arab work (or both) upon Byzantine foundations, and I think it exceedingly likely that the castle of Hâtim Tâi is that Rhabdium which, according to Procopius, was fortified by Justinian. It lay, says he, on a steep rock upon the frontiers of the Roman and the Persian empires, two days from Dara. Below it was the Ager Romanorum, which has been identified with the plain between Môsul and the Tûr 'Abdîn. Since there was no water near it (there is none, as I have said, in the Tûr 'Abdîn), Justinian was obliged to cut a number of cisterns.3
---------------------------
3 The Buildings of Justinian (Palestine Pilgrims' Text Society), p. 51.
---------------------------
The whole of this description exactly fits the castle of Hâtim Tâi, and the presence of Byzantine masonry among the ruins is strongly in favour of the identification. The position of the / p.308 / fortress is exceedingly fine. The hills drop down sharply from its very walls into the Mesopotamian plain, where the long line of the Jebel Sinjâr, a mountain occupied almost exclusively by the Yezîdîs, alone breaks the desolate expanse.
A cruel disillusion awaited us when we reached the valley. The Yezîdîs, who were feasting Jûsef and the zaptieh on bread and bowls of milk, declared that there was no getting to Useh Dereh except by taking the path down into the plain and climbing up into the hills again by a pass at Kal'at ej Jedîd. Even the direction from which we had come was blocked to us, for we refused to contemplate a return through the woods down which we had pushed our way with so much difficulty. The Yezîdîs, who had heard from Jûsef that we had recently visited 'Alî Beg, begged us to stay the night in their caves (the village of Gelîyeh is all underground), and offered to kill a sheep for us, and when I was obliged to decline this eagerly proffered hospitality, one of their number accompanied us for some distance to show us the way. Riding through oak woods where the bees had hived in every hollow trunk we came to a small and dilapidated Yezîdî shrine, where my guide paused to kiss the largest of the trees. "It belongs to the ziyârah," he said in answer to my question. "We do not collect the honey out of any of these trees; all the wood here belongs to the ziyârah." We left Gelîyeh at 10.30 and in two hours found ourselves in the familiar Mesopotamian landscape, an interminable flat strewn with big mounds, each with its village near it. The climate, too, was familiar, and we rode wearily through a burning heat to which we had not thought to return. At 11.30 we passed near Kalka; at 12.30 we came to Kinik, where we spent half-an-hour trying to re-shoe one of our horses. But the farrier was dead, so we were informed, and though we had the shoe with us the whole village could not produce a single nail. When once the Yezîdî was gone none of our party had any special knowledge of the way, but Kiepert (upon whom be praise!) served us well, and with his help we hit off the valley which led up to Kal'at ej Jedîd, and at five o'clock we found ourselves, tired and hungry, under its towers. It / KAL'AT EJ JEDÎD p.309 / soared above us, no less splendidly placed than Kal'at Hâtim Tâi, and guarded this second pass just as Hâtim Tâi had guarded the other. If we had been certain that we should reach our camp before nightfall I should have climbed up to it, but in the mountains no one can make a sure calculation of distances, and we dared not stay. I know nothing, therefore, of Kal'at ej Jedîd but its magnificent outer aspect, and it remains in my memory as a vision of wall and tower and precipitous rock rising into the ruddy sunset light above a shadowy gorge, a citadel as bold and menacing as any that I have seen.1
---------------------------
We led our horses up the rugged gorge, and at 6.40 regained the plateau of the Tûr 'Abdîn. A little village, Bâ Dibbeh, stood at the head of the pass, and before us stretched a rolling, thickly wooded country. We stopped at the village pool to inquire our way, and were given the general direction of Useh Dereh, coupled with a vague assurance that it was not far. The paths were too stony for riding, and to walk was a relief after so many hours of the saddle; I left my companions to bring on the horses and turned into the darkening oak woods. For close upon an hour I followed the course of a shallow winding valley; the trees, standing close about the path, obscured all view; a brooking silence, unbroken by man or beast, hung over the forest, the dark deepened into cool, sweet-smelling night, and still the narrow rocky path wound on between wooded banks. And just as I was wondering whether it had any end, the trees fell back round an open patch of corn and vine, and the lights of my camp shone out upon the further side.
---------------------------
The Jacobite priest of Useh Dereh, when he heard that we proposed to visit Mâr Augen, offered to accompany us, saying that he wished to pay his respects to the bishop who lived there (this was a figure of speech, for the bishop is not to be seen of any man), and he guided us for an hour through the woods to the southern edge of the hills.2
---------------------------
The path to the monastery was a rock-cut staircase, but we succeeded in dragging the horses down it and left them by the gate (Fig. 194). Under the crag stands the church with its tiny cloister and walled court, and it did not take long to discover that, in spite of many rebuildings, the tradition as to its age could not be far wrong. A church must have stood here in the sixth century, if not in the fifth; / MÂR AUGEN p.311 / some of the old capitals have been re-used at a later time, and the ancient plan is preserved in church and cloister. Ten monks are lodged in the rock-cut cells of their remote forerunners—I met with one of them in the cloister and he carried intelligence of my arrival to the prior, who came in haste to do the honours of his church. He was a man of some thirty years of age, with melancholy eyes. We sat together in the shadow of the cloister, while he explained to me the rule under which he and his brethren lived, and as he spoke I felt the centuries drop away and disclose the ascetic life of the early Christian world. They spend their days in meditation; their diet is bread and oil and lentils; no meat, and neither milk nor eggs may pass their lips; they may see no woman—
---------------------------
which stands fortress-like upon the top of a hill. The bishop (for there was a bishop here also—the number of prelates in the Tûr 'Abdîn is scarcely to be reckoned) was singularly unlike his colleagues of the other monasteries. He carried sociability to so high a point that I doubted whether I should be allowed to proceed that day upon my journey, but with the regrettable incident at Mâr Yuhannâ fresh in my memory, I put force upon my appetite and ate the second breakfast upon which his hospitality insisted, while the zaptieh and Jûsef, who were not in the habit of counting breakfasts, did fuller justice to the remains of it. The monastery is a rambling building with a chapel upon an upper floor and a crypt containing the tombs of priors. The tomb of the patron saint is in the church itself. Over it hangs a rude picture of Mâr Melko with the devil beside him: upon inquiry the bishop explained that the saint had been renowned for his power of casting out devils, and he pointed to a collar and chain attached to the wall and observed that men who were afflicted with fits or madness came here to be cured, and all / p.314 / went away sound, no matter what their creed.
1
---------------------------
The buildings bore evidences of frequent reconstruction, and parts of the church were still in the state of ruin in which a recent Kurdish raid had left them. It is almost impossible to date architecture of this kind, for the new work and the old have much the same character, but the plan of the church is the ancient monastic scheme, as I learnt at Mâr Gabriel and at Salâh, and in all probability Mâr Melko is to be counted among the oldest foundations of the Tûr 'Abdîn. Like Mâ Gabriel it is some distance removed from the nearest village, and depends for its security upon its own strong walls. After we had passed through Kharabah 'Aleh, which contains the ruins of a church, we wandered among the rolling, wooded hills, and had gone needlessly far to the north before we caught sight of the monastery of Mâr Gabriel standing upon an eminence, with my tents pitched beside it. The inevitable bishop was away and I could not regret his absence, since it implied a relaxation of the social duties which I should otherwise have been obliged to fulfil, and permitted me to give my whole attention to the building.
1 I would suggest that Kal'at ej Jedîd may occupy the site of the Sisaurana of Procopius, which was destroyed by Belisarius. Sisaurana, however, lay three miles from Rhabdium, and even as the crow flies the distance between K. Hâtim Tâi and K. ej Jedîd must be greater. But the important position of K. ej Jedîd on one of the few passes up from the plain suggests that the spot must have been fortified in ancient times. Sisaurana is no doubt the Sisara of Ammianus Marcellinus: see Ritter, Vol. XI. p. 150 and pp. 400-401.
---------------------------
If we had travelled far in the body upon that day, we travelled further in the spirit upon the next. There lies upon the lip of the hills, overlooking the wide desolation of Meso- / p.310 / potamia, a monastery which is said to be the mother house of all the Tûr 'Abdîn. Into these solitudes, according to the tradition of the mountain, wandered at the beginning of the fourth century a pupil of St. Antony, whose name was St. Eugenius. He had learnt from his master the rule of solitude and had overcome with him the devils that people the Egyptian sands; among the rocks of Mount Izala he laid down his pilgrim's staff, gathered disciples about him and founded the monastery that still bears his name. It was at first no more than a group of cells hollowed out of the cliff, but as its fame increased, the monks built themselves a church upon a narrow shelf between precipice and precipice, and helped out the natural defences of the mountain by a strong wall of masonry. The cave cells increased in number until the rocks were honeycombed on every side, and disciples of the first founder led forth companies of monks to raise fresh monasteries over the Tûr 'Abdîn.1
1 Though tradition links these foundations with Egypt, it is quite possible that they may have had a yet closer connection with Syria, where in the fourth century monasticism and the solitary life had already taken a strong hold. Duchesne: Histoire de l'Eglise, Vol. II. p. 516.
---------------------------
2 Kiepert marks a "Gr. Cænobium van Izala," which is, I imagine, intended for Mâr Augen, but its position relatively to K. ej Jedîd and Useh Dereh, as marked in the map, cannot be correct. Mâr Yuhannâ, which lies to the east of Mâr Augen, approaches more nearly to Kiepert's site. I have published a short account of these and other monasteries and churches of the Tûr 'Abdîn in Amida (Strzygowski and Van Berchem).
---------------------------
"But may you see me?" I asked.
"We have made an exception for you," explained the prior. "Travellers come here so seldom. But some of the monks have shut themselves into their cells until you go."
The cell of St. Eugenius stands apart from the others, hollowed out of the cliff to the west of the church. The prior had spent a lonely winter there, seeing no one but the brother who brought him his daily meal of bread and lentils. As we stood in the narrow cave, which was more like a tomb than a dwelling-place. , I looked into the young face, marked with the lines drawn by solitude and hunger.
"Where is your home?" I asked.
"In Mardîn," he answered. "My father and my mother live there yet."
"Will you see them again?" said I.
"Perhaps not," he replied, but there was no regret in his voice.
"And all your days you will live here?"
He looked out calmly over rock and plain. "Please God," he said. "It seems to be a good place for prayer."
It is the habit of the monks to let no traveller depart without food, a habit well known to the neighbouring Kurds who claim more hospitality than the monastery can well afford. While I worked at the church, the prior betook / p.312 / himself to the cave kitchen and prepared an ample meal of eggs and bread, raisins and sour curds for me and for my men. When we had eaten I asked whether it would not be seemly to thank the bishop for the entertainment which had been offered to us.
"You cannot see him," said the prior. "He has left the world."
"The kas from Useh Dereh came to-day to visit him," I objected.
"He came to gaze upon his cell," answered the prior, and with that he led me out of the church and pointed to a cave some fifty feet above us in the cliff. Three-quarters of the opening had been filled with masonry, and I could see that it was approached by a stair of which the lower part was cut out behind a gallery and the upper on the face of the rock. An active novice might have thought twice before attempting the path to the bishop's cell.
"Is he old?" said I.
"He is the father of eighty years," replied the prior, "and it is now a year since he took a vow of silence and renounced the world. Once a day, at sunset, he lets down a basket on a rope and we place therein a small portion of bread."
"And when he dies?" I asked.
"When he is sick to death he will send down a written word telling us to come up on the next day and fetch his body. Then we shall see his face again."
"And you will take his place?" said I.
"If God wills," he answered.
We walked across the hills for half-an-hour to Mâr Yuhannâ, a monastery founded by a disciple of St. Eugenius. It is neither so finely placed nor so interesting architecturally as Mâr Augen, though the rough walls of church and monastic building, which cling to the rocky slopes are not without a certain wild beauty. The bishop who rules over the house of Mâr Yuhannâ is less exclusive than the prelate at Mâr Augen, for he shares a tower with his four monks, but he was still too exclusive to receive my visit. The aged prior was all for serving us with a meal, but I could not / MÂR YUHANNÂ p.313 / undertake to dispose of another omelet, nor did I realize that my refusal would be regarded as a shocking breach of the social code. The prior was so deeply hurt that he would not bid us farewell, and we left under the cloud of his displeasure. We climbed back to the summit of the hills and rode home to Useh Dereh, and if any one should wonder why a recluse from Egypt should have sought so distant a dwelling-place as Mount Izala, I can give a sufficient answer. It was because he found Iris Susiana growing among the rocks. The great grey flowers lift their heads in every open space between the oak-trees, gleaming silver in the strong sun, and so perfect are they in form, so exquisite in texture, that I stood amazed at the sight of them, as one who gazes on a celestial vision.
It is just an hour's ride from Useh Dereh to Mâr Melko,
1
1 Kiepert places Mâr Melko too far from Useh Dereh. My itinerary was as follows: Useh Dereh to Mâr Melko, 1 hr.; Mâr Melko to Kharabah 'Aleh, 30 min.; Kharabah 'Aleh to Kernaz, 2 hrs. 15 min.; Kernaz to Deir el 'Amr, 1 hr. 15 min. All these places are marked in the map.
---------------------------
1 Niebuhr heard that Mâr Melko was famed for the curing of epilepsy: Reisebericht, Vol. II. p. 388. Not having penetrated into the Tûr 'Abdîn, he thought that the report that there were seventy monasteries in the hills must be an exaggeration, but I expect that it was not far from the truth.
---------------------------
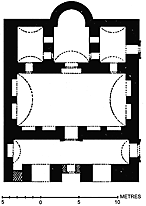
The house of St. Gabriel of Kartmîn was, during the Middle Ages, the most famous and the richest of Jacobite establishments. It is said to have been founded in the reign of Arcadius (395-408) and rebuilt under Anastasius (491-518), and I see no reason to doubt that the great church of Mâr Gabriel is, as it now stands, a work of the early sixth century. There are two other churches within the existing monastic precincts, one dedicated to the Virgin, the other to the Forty Martyrs, but neither of these is as old as that which is dedicated to the tutelary saint (Fig. 197). A large area of ruins beyond the walls gives some indication of the former magnificence of the monastery which gained, as early as the days of Justinian, a reputation for holiness second only
[ Illustrations opposite p.314 ]

|

|
[ Illustrations opposite p.315 ]

|

|
/ MÂR GABRIEL p.315 / to Jerusalem. It bore at that period the name of St. Stephen; St. Gabriel was bishop of the monastery during the reign of Heraclius. When the Arab invaders drove out the forces of the Byzantine empire, he obtained from the Khalif 'Umar ibn u'l Khattâb rights of jurisdiction over all Christians in the Tûr 'Abdîn, for which reason the monastery is sometimes called after him, Deir Mâr Gabriel, and sometimes after the khalif, Deir 'Umar. It was despoiled by Timûr towards the close of the fourteenth century, and many a harrying it must have endured from the Kurds before it sank into its
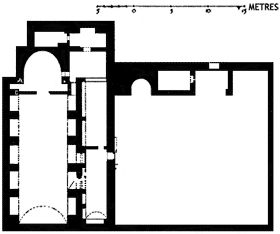
PARISH CHURCH.
|
MONASTIC TYPE. |
---------------------------
and camped beside the ruined church of Mâr Philoxenos which, since it has not been recently repaired, is of greater interest than any other in the town.2
---------------------------
/ p.316 / The task of planning it was a labour of hatred. The population of Midyâd, men, women and / MIDYÂD p.317 / children, stationed themselves upon the ruined walls, and for them it was no doubt the most entertaining afternoon which they had spent for many a long week, but for me, and for the patient bearers of the measuring tape, the hours were charged with exasperation. The Kâimmakâm, when he appeared upon this agitated scene (Midyâd is the seat of government in the Tûr 'Abdîn), succeeded in clearing the ruins for a few moments, but as soon as he had turned his back, the hordes reassembled with a greater zest than before.
1 Deir 'Umar, 5.30; Mezîzakh, 8.15; Midyâd, 9.15.
---------------------------
2 I visited inside the town Mâr Shim'ûn, which is in process of being rebuilt, and Mâr Barsauma, which has been completely rebuilt. Outside the town is the monastery of Mâr Ibrahîm and Mâr Hôbel. It has recently been repaired, but much of the masonry is ancient. The two churches, dedicated to the two patron saints, belong to the monastic type of Mâr Gabriel; the mouldings round the doors, and the cyma cornice are old. There is also a small chapel, dedicated to the Virgin; it is square in plan and covered by a dome on squinches, but it appeared to me to be of later date. I was shown in this monastery a / p.317 / very remarkable silken vestment. The ground is of green satin covered with a repeated pattern in gold, silver and coloured silks, representing a woman in a red robe seated in a howdah upon the back of a camel. A man naked to the waist is seated upon the ground with his head bowed upon his hands. A variety of animals and floral motives are scattered round the principal figures. The subject is no doubt taken from the story of Leila and Majnûn. The date of this brocade is probably somewhere between 1560 and 1660. A fragment showing a like pattern is in the possession of Dr. Sarre. The monastery possesses besides a small bronze thurible, of which I succeeded in procuring a counterpart. A similar thurible exists in the British Museum (No. 540 in the catalogue of Early Christian and Byzantine Antiquities); it is said to have come from Mâr Musa el Habashi, between Damascus and Palmyra. The Kaiser Friedrich Museum has obtained several in Cairo and Trebizond (Wulff: Altchristliche Bildwerke, Teil I, nos. 967-970). These are ascribed to the sixth and seventh centuries. Mr. Dalton, to whom I owe this information, gives me references to two others, one in the Bargello collection at Florence (No. 241 in the catalogue of the Carraud Collection, published in 1898) and one published in the Echos d'Orient, VII., 1904, p. 148.
---------------------------
My Christian servants returned in the evening from the bazaar gravely disquieted by the gossip which was current there. It was rumoured that the wave of massacre had spread to Aleppo and they trembled for the fate of their wives and families. The news which was causing us so much anxiety was in fact nearly a month old, but we did not learn until we reached Diyârbekr that Aleppo had escaped with a week of panic.
The next day was devoted to three churches which I visited and planned on the way to Khâkh, Mâr Yâ'kûb at Salâh, Mâr Kyriakos at Arnâs and Mâr 'Azîzîyeh at Kefr Zeh. I doubt whether there exists anywhere a group of buildings / p.318 / more precious to the archæologist than these three churches and the little domed shrine of the Virgin which stands almost perfect among the ruins of Khâkh (Fig. 201). It is close upon a miracle that in this forgotten region, long subjected to the tyranny of the Kurds, such masterpieces of architecture should have escaped destruction; the explanation is probably to be found in the rugged mountain frontiers of the Tûr 'Abdîn. Even though it lay upon the edge of country which was for over a hundred years the battle-ground of the Persian and the Byzantine, war seems to have penetrated but little into its heart. The Christian communities, from
their rock-cut cells in the crags of Mount Izala, must have listened to the rumours of advance and flight and siege; they could almost witness the encounter of armies in the plain below. But "the lofty mountain, precipitous and almost inaccessible," as Procopius describes it, was a sure refuge, and Procopius himself can scarcely have been acquainted with the wooded uplands and fertile valleys where already in his time stood the churches and monasteries of Salâh and Arnâs, Kefr Zeh and Khâkh. The Arab conquerors left the Christians undisturbed; they bowed the head and suffered under the fierce blast of Tîmûr's invasion and under the secular persecution of the Kurds; but decimated and stripped of their wealth, they held firmly to the bare walls of their religious houses, and the meagre, ragged choirs still chant their litanies under vaults which have withstood the assault of fourteen centuries. Into this country I came, entirely ignorant of its architectural wealth, because it was entirely unrecorded. None of the inscriptions collected by Pognon go back earlier than the ninth century; the plans which had
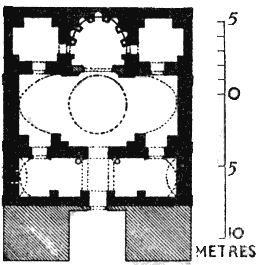
THE VIRGIN
[ Illustrations opposite p.318 ]

|

|
[ Illustrations opposite p.319 ]

|

|
[ Illustrations opposite p.322 ]

|

|
[ Illustrations opposite p.323 ]

|

|
---------------------------
and a day upon the walls, which are as fine an example of mediæval fortification as any that exists. They hang, upon the south and south-east sides, high over the Tigris—it was from this direction that Sapor's troops effected an entry through a hollow passage that led down to the water's edge. On the south-west they crown a slope set thick with gardens of mulberry and vine, and towards the north the wall bends round to join the curve of the river. Four great gateways break this circuit. The Mardîn Gate commands the terraced gardens, and the road that passes through it runs down to an ancient bridge over the Tigris (Fig. 206). To the north-west and north the Aleppo or Mountain Gate and the Kharpût Gate open on to a fertile plain, and the Yeni Kapu, the New Gate, stands above the precipitous southern bank (Fig. 207).2
---------------------------
The lie of the ground makes it certain that the oldest fortifications of the city must have occupied much the same position as those which still surround it, and though the latter are proved by numerous inscriptions to be Mohammadan work of different periods, I should judge them to be built mainly upon ancient foundations. The north wall with its round towers is perfectly preserved; even the domed chambers inside the towers, together with the stairs that gave access to the chemin de ronde, are intact. All the arches and domes in the interior of the towers are of brick. Between the Kharpût and the Aleppo Gates a small aqueduct brings water to the town, the few springs within the walls being unpleasantly brackish. The citadel commands the north-east angle above the river; most of the space surrounded by its enclosing wall is occupied by modern buildings and by a mound whereon stood the castle of the first Mohammadan princes. The domed arsenal is said to have been a Christian / DIYÂRBEKR p.325 / church, but remembering my unsuccessful attempts to visit the arsenal at Baghdâd, I did not ask permission to enter it.1
---------------------------
From a postern gate in the north wall a road leads down to the river, passing under a cliff out of which gushes a sulphurous spring. As I watched the soldiers of the garrison washing their clothes in its waters, I tried to reconcile it with "the rich spring, drinkable, indeed, but often tainted with hot vapours," which Ammianus Marcellinus describes as rising under the citadel, and to see the men of the 5th Parthian Legion in the ragged groups standing about it.2
---------------------------
From the citadel we walked to the Mardîn Gate along the chemin de ronde, a fine course, lifted high above the close air of the city and swept by the breezes that come down from Taurus (Fig. 208). Between the Aleppo Gate and the Mardîn Gate stand two huge round towers, larger than any others and later in date.3
---------------------------
Near the Mardîn Gate the chemin de ronde is for some distance vaulted over and lighted only by small loop-hole windows on the inner side. To the south of the Mardîn Gate the wall runs out abruptly, and the salient angle thus formed holds a great hall of which the vault is borne on columns. The two main streets lie from gate to gate, intersecting each other at right angles, and since this is in accordance with an ancient scheme of city planning, the line of the streets may be as old as the first foundation of the town. Not far from the point of intersection stands the Ulu Jami' with its famous courtyard, enclosed to east and west by a two-storeyed portico, which has been conjectured to be either the remains of a church built by Heraclius or a Byzantine palace (Fig. 209). The buildings need a more exhaustive / p.326 / study than the fanaticism of the Mohammadan population will at present admit, and the correct plan of mosque and court has yet to be made. The older part of the work is closely related to the ancient architecture of the Tûr 'Abdîn.
/ DIYARBEKR p.323 / come to Midyâd to help me out of difficulties. A cheerful travelling companion he proved, and a well-informed. We camped on the second evening under the mound of Karkh, not far from the Tigris, and shortened our way next day by fording the river, which was now a shallow stream, and cutting across a wide bend (Fig. 205). This route had the advantage of giving us a first view of Diyârbekr under its finest aspect. It stands upon the high crest of the Tigris bank, a great fenced city built of basalt—"black are the dogs and black the walls and black the hearts of black Amid," says the proverb. Since the days when Ammianus Marcellinus took part in the desperate resistance to Sapor, and watched from the towers of Amida the Persian hosts "collected for the conflagration of the Roman world," the din of battle has never been far from Diyârbekr. The town passed to and fro between the Byzantine and the Sassanian. Constantius fortified it and lost it to Sapor; Anastasius recaptured it and lost it to Kobâd and won it back; Justinian rebuilt the fortifications, but it fell with Mesopotamia to the Moslem invaders. The Kurdish Marwânds made it their capital, and after them the Turkmân Ortukids; Tîmûr burst through the famous walls and put the inhabitants to the sword, and finally the Turk conquered it in A.D. 1515 and holds it still. But there is no peace for the lawless capital of Kurdistân. Warring faiths struggle together as fiercely as rival empires, and the conflict is embittered by race hatreds. The heavy air, lying stagnant between the high walls, is charged with memories of the massacres of 1895, and when I was in Diyârbekr the news from Cilicia had rekindled animosity and fear. Moslem and Christian were equally persuaded that the other was watching for an opportunity to spring at his throat. Tales of fresh outbreaks in different parts of the empire were constantly circulated in the bazaars, and the men who listened went home and fingered at their rifles. If there had been any sign of further disturbance at Constantinople, Diyârbekr would have run with blood.
With the population in this temper it would have been futile to inquire into the prospects of constitutional govern- / p.324 / ment. I spent a day among ancient churches;1
1 I have published photographs and plans of the Jacobite church of the Virgin and the Greek Orthodox church of Mâr Cosmo in Amida: Van Berchem and Strzygowski.
---------------------------
2 The Yeni Kapu differs in plan from the other three. It has square bastions, whereas they are protected on either side by massive round towers. The round towers extend all along the northern parts of the wall; on the other sides the towers are rectangular.
---------------------------
1 A sketch plan, made by De Beylié is published in Amida.
---------------------------
2 His phrase "under the citadel but in the very heart of Amida" is difficult to understand. It does not seem to imply a spring outside the walls, yet there is no place "under the citadel" and within the walls.
---------------------------
3 One is known by inscriptions to have been erected by the Ortokid Sultan Malek Shah in the year A.D. 1208-1209, and the other must belong to the same period. The inscriptions have been published by Van Berchem, see Lehmann-Haupt: Materialen zur älteren Geschichte Armeniens und Mesopotamiens, p. 140. They are more fully published in Amida, but that work has not appeared in time for me to make any accurate reference to it.
---------------------------
Even this hasty survey of Diyârbekr was sufficient to convince me that the treasures which it contains are still unexplored. Of its many mosques only the Ulu Jami' has been so much as photographed, though the square minarets scattered over the town are probably an indication of an early date. Once or twice as I walked in the bazaars I looked through gateways into the courts of splendid khâns, where the walls were decorated with contrasted patterns in limestone and basalt, and stripes of black and white masonry are used in many of the houses and mosques. The final history of Amida must wait upon a much more careful investigation of the town than any which has yet been undertaken.